What Is the 5G Pipe Qualification?
The AWS D1.1 5G pipe qualification is a groove weld test performed on a pipe coupon fixed with its axis horizontal. The pipe cannot be rotated — the welder moves around the full circumference, welding through every position from the bottom upward. The "5" designates the horizontal fixed position. The "G" designates groove weld.
Unlike plate testing, where each test addresses one position, the 5G forces the welder to handle three positions continuously in a single weld — starting near-flat at the bottom, transitioning through vertical on both sides, and finishing overhead at the top. There is no opportunity to stop and re-setup between positions. It is a real-world pipe welding simulation and a significant step up from plate qualifications.

What the 5G Qualifies You For
One coupon covering three groove positions and three fillet positions. The 5G does not cover 2G horizontal — that requires either a separate 2G plate test or the 6G pipe qualification.
| Test | 1G | 2G | 3G | 4G | 5G | 6G | 1F | 2F | 3F | 4F |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 5G Pipe Test | ✓ | ✗ | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | ✗ | ✓ | ✗ | ✓ | ✓ |
| 6G Pipe Test | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ |
5G vs. 6G — Which Do You Need?
This is the question most pipe welders face. The honest answer: it depends on what your production work actually requires.
| Factor | 5G | 6G |
|---|---|---|
| Pipe Angle | Horizontal (0°) | Inclined (45°) |
| 2G Horizontal Covered | No | Yes |
| All Pipe Positions | No (missing 2G) | Yes — complete |
| Difficulty | High | Highest |
| Accepted in lieu of 5G? | N/A | Yes — always |
| 5G accepted in lieu of 6G? | Never | N/A |
| Best for | Flat/vertical/overhead pipe work | All-position pipe work |
| Gold standard? | No | Yes |
The 5G is a legitimate, widely accepted qualification for structural pipe work. If your welders will not be working on horizontal pipe groove welds and the project specs don't require 6G specifically, the 5G gets the job done with a less demanding test. If you want complete coverage and never want to think about this again, qualify the 6G.
Test Coupon Specifications
Welding Processes for the 5G Test
Process selection on the 5G matters — each pass around the pipe involves position changes that affect puddle behavior differently across processes. SMAW is the most common choice for structural 5G testing for good reason.
SMAW — E6010 Root / E7018 Fill & Cap
- Most common and universally accepted for structural 5G testing
- E6010 root: forceful arc, fast-freeze slag, penetrates open root gap cleanly
- E7018 fill and cap: low hydrogen, controlled puddle through all positions
- Clean restarts mid-pass — essential when repositioning around the pipe
- E6010 requires DC+ polarity — verify your machine setting before testing
- Store E7018 in rod oven — moisture causes porosity and hydrogen cracking
GTAW Root / SMAW Fill & Cap
- TIG root produces the cleanest root bead geometry on pipe
- Preferred where higher quality requirements or radiographic testing applies
- Slower than SMAW root — but root pass quality directly controls bend test results
- More physically demanding through the overhead section of the 5G
- Transition from GTAW root to SMAW fill is a critical interpass step
- Common in power generation, pressure vessel, and high-integrity structural work
FCAW
- Higher deposition rate — faster groove fill than SMAW
- FCAW-G (gas-shielded) for controlled environments
- FCAW-S (self-shielded) where wind affects shielding gas
- Puddle control through overhead section requires significant FCAW pipe experience
- Slag management around full circumference takes more time and attention
- Only recommended for welders with established FCAW pipe experience
Process Selection Notes
- Test on the process you use in production — qualification must match actual work
- Each process qualifies separately — SMAW cert does not cover FCAW production welding
- For most structural D1.1 pipe testing, SMAW E6010/E7018 is the right answer
- GTAW root is worth it if radiographic testing is part of the quality program
- If you're uncertain, call us — we'll help you match the test to your application
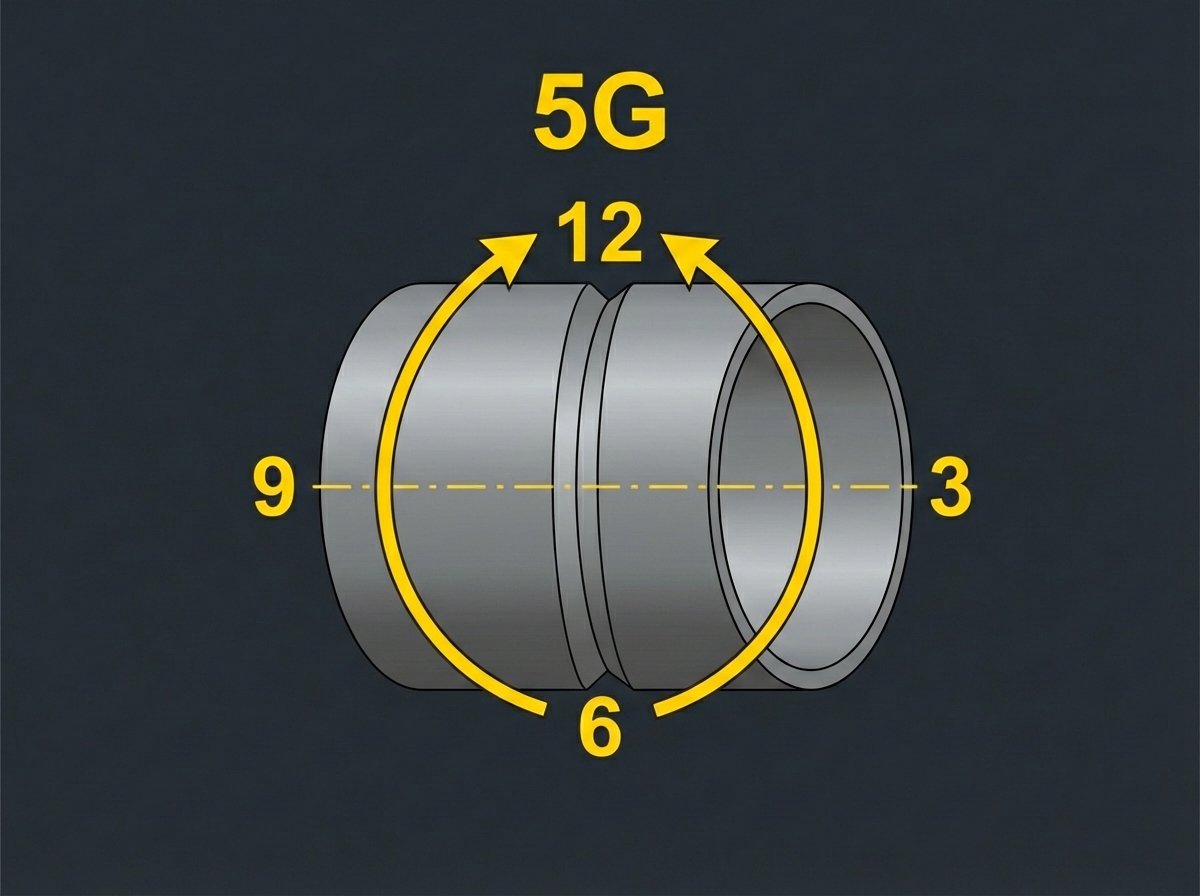
Technique — Moving Around the Pipe
The 5G weld starts at the 6 o'clock position at the bottom of the pipe. The welder completes one half of the circumference — from 6 o'clock up to 12 o'clock — then returns to 6 o'clock and completes the other half upward to 12 o'clock. Both half-passes start at the bottom and travel upward to the top.
6 O'Clock — Bottom Start
- Begin both half-passes at the 6 o'clock position
- Bottom of the pipe is near-overhead on the 5G — treat it like overhead technique
- Tacks at 3, 6, 9, and 12 o'clock — grind tack starts and stops flush before welding
- Root pass: tight arc, watch the keyhole for consistent back-side penetration
- Establish travel speed rhythm before reaching the vertical transition
3 and 9 O'Clock — Vertical Zones
- True vertical position at the 3 and 9 o'clock sides of the pipe
- Use uphill vertical technique — consistent stringer, no weave
- Work angle perpendicular to pipe surface throughout
- Travel speed naturally wants to slow down — resist it, keep consistent
- Interpass cleaning at vertical sections — slag tends to trap at the lower bead edge
12 O'Clock — Overhead Zone
- True overhead at the 12 o'clock top — the hardest section of the 5G
- Reduce amperage slightly as you approach the top
- Shorten arc length — puddle will sag if arc gets long overhead
- Keep beads narrow — stringer only, no weaving overhead
- The two half-passes meet here — tie-in cleanly, no high spot
- Practice the 12 o'clock transition specifically before test day
Root Pass — The Foundation
- E6010 root: aim at the root gap, let the keyhole tell you if penetration is right
- Consistent keyhole size around the full circumference = consistent root bead
- If keyhole closes, slow down; if it opens too wide, speed up
- Grind any high spots or rough restarts before fill passes
- Root pass failure on bend test is the most common 5G test failure
- No skipping — if the root pass looks wrong, stop and discuss before proceeding
Common 5G Test Failures
Cold Lap or Incomplete Fusion at Overhead (12 O'Clock)
The most common 5G visual and bend test failure. As the welder approaches the overhead section, travel speed and arc length changes cause the puddle to bridge over the joint without fully fusing — cold lap at the weld toes. Fix: Slow approach to the overhead zone, shorten arc length aggressively, focus on seeing the puddle wet into both plate edges before traveling forward.
Poor 12 O'Clock Tie-In Between Half-Passes
Where the two half-passes meet at the top is a common failure point. One side stops too high or too low, the other can't tie in cleanly — cold lap or slag trap at the junction. Fix: Grind the end of the first half-pass flush before starting the second. Run the second pass into the first with a brief pause to ensure full fusion at the tie-in point.
Incomplete Root Penetration
Root pass fails the bend test — specimen opens along the root where fusion was incomplete. Most common in the transition zones between vertical and overhead. Fix: Maintain consistent keyhole throughout the root pass — if the keyhole disappears at any point, full penetration is not being achieved. Adjust travel speed immediately.
Slag Inclusions from Incomplete Interpass Cleaning
Welding around a full pipe circumference means chipping and brushing in awkward positions. Slag that accumulates on the lower edge of each stringer must be fully removed before the next pass. Fix: Chip and wire brush every pass on the full circumference. Use a grinder on tight corners. Do not weld over incomplete slag removal.
Undercut at Cap Pass Toes in Overhead Zone
Undercut exceeding 1/32" at weld toes is automatic visual rejection. Most common at the overhead section where travel speed tends to increase and arc length extends. Fix: Consistent cap pass travel speed around the full circumference. Reduce amperage slightly from fill pass settings and pause briefly at each toe in the overhead zone.
Arc Strikes Outside Weld Zone
Automatic visual rejection per D1.1 Clause 4.9 — no exceptions. More common on pipe than plate because the welder must reposition multiple times during a full circumference weld. Fix: Strike the arc inside the joint every time without exception. Inspect the full pipe surface carefully before shipping.
Visual Inspection Requirements
| Discontinuity | Limit | Notes |
|---|---|---|
| Cracks | None permitted | Any crack = immediate rejection |
| Incomplete fusion | None permitted | Anywhere in joint |
| Cold lap | None permitted | Most common 5G overhead failure |
| Undercut | ≤ 1/32" (0.8mm) | Full circumference |
| Reinforcement | ≤ 3/16" (4.8mm) | Outside diameter surface |
| Arc strikes | None outside weld zone | Automatic rejection |
| Root concavity | ≤ 1/16" per D1.1 | Inside diameter surface |
Bend Testing the 5G Coupon
Coupons passing visual proceed to accredited laboratory bend testing. Specimens are cut from specific clock positions around the circumference per D1.1 Table 6.13 — including specimens from the overhead zone where failures are most likely. All specimens must pass.

Certification Validity — The 6-Month Rule
Per AWS D1.1 Clause 4.25, the 5G qualification is valid indefinitely as long as the welder uses the qualified welding process at least once every six months and the employer documents it in a continuity log. If more than six months passes without using the process, the qualification expires and retesting is required.
Industries That Require the 5G Qualification
Structural Steel Contractors
Pipe columns, hollow structural sections, and round HSS connections in structural steel frames require pipe qualification under D1.1. The 5G is specified on structural steel projects where pipe connections will be welded in fixed positions.
Industrial Piping
Process piping in industrial facilities, refineries, and power plants involves pipe groove welds in fixed positions. The 5G qualification covers flat, vertical, and overhead — the three positions most commonly encountered in industrial pipe work.
Shipbuilding
Hull and systems piping in shipyards involves pipe in fixed orientations throughout the vessel. The 5G qualification is accepted for most shipyard structural pipe work under D1.1.
Heavy Construction
Bridges, stadiums, arenas, and large commercial construction involving structural pipe connections frequently specify pipe qualification. The 5G covers the majority of fixed pipe positions encountered on heavy construction projects.
Mail-In Service — How It Works
-
Contact us for WPS and quote
Confirm process (SMAW, GTAW root, FCAW) and pipe specs. We provide a qualified WPS and pricing. You may use your company's existing D1.1 pipe WPS if it covers the 5G position.
-
Weld the 5G coupon at your facility
Your welder completes the full circumference weld on the horizontally fixed pipe coupon per the WPS. Proper fit-up, tacking, and interpass cleaning are the welder's responsibility before shipping.
-
Ship the completed coupon
Follow our shipping instructions. Pipe coupons ship standard ground. Include welder name, process, and contact information with the shipment.
-
CWI visual inspection
Our AWS CWI performs full visual inspection per D1.1 Clause 4.9. We contact you on any visual rejection before proceeding to bend testing.
-
Accredited bend testing
Specimens cut from required clock positions, prepared, and bent per D1.1 at our accredited testing laboratory. Full documentation of results.
-
WPQ issued and delivered
CWI signs and issues the official WPQ on passing. Delivered by email and mail. See timeframes for current turnaround.
Glossary
Pipe fixed with its axis horizontal. The welder moves around the full circumference through flat, vertical, and overhead positions. The pipe cannot be rotated during welding.
Root pass welded from the outside of the pipe only, with no backing ring. Full penetration and a sound root bead on the inside surface must be achieved from the outside alone.
The small hole visible ahead of the weld puddle during open root pipe welding. Confirming a consistent keyhole throughout the root pass verifies full penetration and a sound root bead on the inside surface.
Weld metal that bridged over the joint surface without fusing to the base metal — creates a visual discontinuity along the weld toe. Automatic rejection per D1.1. Most common in the overhead zone of the 5G test.
Cellulosic SMAW electrode preferred for open root pipe passes. DC+ polarity, fast-freeze slag, penetrating arc. The standard choice for structural pipe root passes.
Welder Performance Qualification record — the official CWI-signed document certifying the welder passed the 5G test. Lists all positions covered, process, pipe size, and thickness range qualified.
Employer-maintained record documenting that the welder has used the qualified process at least once every six months. Required by D1.1 Clause 4.25 to maintain qualification validity.
Pipe fixed at 45-degree incline — the more comprehensive and more difficult pipe test. Covers all positions including 2G horizontal. Always accepted in lieu of 5G. See our 6G qualification page.
Frequently Asked Questions
What positions does the 5G pipe qualification cover?
What is the hardest part of the 5G test?
Should I take the 5G or go straight to the 6G?
What process is recommended for the 5G test?
Can I mail in my 5G pipe coupon?
Does the 5G cover the 2G horizontal position?
How long does the 5G qualification stay valid?
What if the welder fails the 5G test?
Do I need a WPS for the 5G test?
Can a 5G qualification transfer to a new employer?
Ready to Qualify for Fixed Pipe Welding?
Mail-in service. CWI inspected. Official WPQ issued. Nationwide.
Need all pipe positions? The 6G qualification covers everything including 2G horizontal.